Categories
Tags
-
#Waste Oil to Diesel
#Land Rig Installation
#Used Engine Oil Recycling
#Transformer Oil Dehydration
#Sodium Fusidate
#Lube Oil Refining
#Dabigatran
#Fire-Resistant Oil Filtration Machines
#Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients
#Dry Air Generator
#Dry Air Generators
#Transformer Oil Filtration Machine
#Base Oil Extraction
#Drum Scales
Archives
Sodium Fusidate API: A Key Player in Antibacterial Formulations
-
Antibacterial formulations play a pivotal role in combating bacterial infections, and among the arsenal of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), Sodium Fusidate stands out as a potent antimicrobial agent. In this article, we will delve into the significance of Sodium Fusidate as an API, exploring its characteristics, mechanisms of action, therapeutic applications, and its role in formulating effective antibacterial medications.
I. Unveiling Sodium Fusidate
- Introduction to Sodium Fusidate API
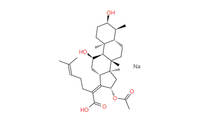
Sodium Fusidate is a sodium salt derived from fusidic acid, a naturally occurring antibiotic produced by the fungus Fusidium coccineum. This API exhibits powerful antibacterial properties, making it an essential component in the development of pharmaceutical formulations aimed at treating bacterial infections.
- Characteristics of Sodium Fusidate
Sodium Fusidate possesses unique characteristics that contribute to its effectiveness in antibacterial formulations:
- Chemical Structure: The chemical structure of Sodium Fusidate features a steroid-like core with a fusidane nucleus. This distinctive structure plays a crucial role in its mechanism of action, allowing it to target specific bacterial processes.
- Mechanism of Action: Sodium Fusidate operates by inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. It specifically targets the elongation factor G (EF-G) in bacteria, disrupting the translation process and preventing the formation of functional proteins. This mechanism makes Sodium Fusidate particularly effective against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive bacteria.
II. Role of Sodium Fusidate in Antibacterial Formulations
A. Therapeutic Applications
Treatment of Skin Infections: Sodium Fusidate is commonly used in the treatment of various skin infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria. Its ability to penetrate skin tissues makes it effective against conditions such as impetigo, cellulitis, and infected dermatoses.
Bone and Joint Infections: Due to its excellent tissue penetration, Sodium Fusidate is employed in the management of bone and joint infections. Its capacity to reach high concentrations in these tissues enhances its efficacy in treating infections affecting bones and joints.
Systemic Infections: In systemic infections, Sodium Fusidate is utilized as part of combination therapy to address bacterial strains resistant to other antibiotics. Its unique mechanism of action makes it a valuable addition to treatment regimens for serious systemic infections.
B. Sodium Fusidate in Antibacterial Formulations
Combination Therapies: Sodium Fusidate is often used in combination with other antibiotics to broaden the spectrum of coverage and mitigate the development of resistance. Combining Sodium Fusidate with other antibacterial agents enhances the overall efficacy of the formulation.
Topical and Systemic Formulations: Sodium Fusidate is available in various formulations, including topical creams, ointments, and systemic preparations such as oral tablets. The versatility of Sodium Fusidate allows for tailored formulations based on the nature and severity of the bacterial infection.
III. Challenges and Considerations
- Resistance Concerns
While Sodium Fusidate remains effective against many bacterial strains, the emergence of resistance is a concern. Continuous monitoring and judicious use of Sodium Fusidate, particularly in combination therapies, are crucial to mitigate resistance and preserve its efficacy.
IV. Conclusion
Sodium Fusidate API stands as a stalwart in the realm of antibacterial formulations, offering a unique mechanism of action and versatility in treating a range of bacterial infections. Its role in combination therapies, coupled with its efficacy in both topical and systemic formulations, highlights its significance in modern medicine. However, vigilance in addressing resistance concerns is paramount to ensuring the sustained effectiveness of Sodium Fusidate in the fight against bacterial infections. As research continues, Sodium Fusidate remains a key player in the evolving landscape of antibacterial agents, contributing to the ongoing battle against infectious diseases.